PHYSICAL EDUCATION (048)
Class XII
Pre-Board Examination (2024-25)
TIME ALLOWED: 3 HRS MAX. MARKS: 70
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS:
1) The question paper consists of 5 sections and 37 Questions.
2) Section A consists of question 1-18 carrying 1 mark each and is multiple choice questions. All questions are compulsory.
3) Sections B consist of questions 19-24 carrying 2 marks each and are very short answer types and should not exceed 60-90 words. Attempt any 5.
4)Sections C consist of Question 25-30 carrying 3 marks each and are short answer types and should not exceed 100-150 words. Attempt any 5.
5)Sections D consist of Question 31-33 carrying 4 marks each and are case studies. There is internal choice available.
6)Section E consists of Question 34-37 carrying 5 marks each and are short answer types and should not exceed 200-300 words. Attempt any 3.
SECTION – A(1*18=18)
1. In a knockout tournament, if 31 teams are participating, how many teams will be in the 4th quarter? (a) 4 (b) 6 (c) 7 (d) 8
2. Frequent menstruation is known as:
(a) Metrorrhagia (b) Oligomenorrhea (c) Polymenorrhea (d) Menorrhagia
3. Parabola is-
(a) The path of an object projected into free air
(b) Path of the object formed with air resistance
(c) Path of object falling vertically down
(d) None of the above
4. Which of the following is a distinctive feature of the Deaflympics compared to the Paralympics and Special Olympics?
(a) Focuses on intellectual disabilities rather than physical impairments.
(b) Prioritizes athletes with a specific range of hearing loss for fair competition.
(c) Utilizes visual cues and sign language for communication and coordination.
(d) Emphasizes the integration of athletes with and without disabilities in all events.
5. Which nutrient is the chief fuel for muscular contraction?
(A) Carbohydrates (B) Fats (C) Proteins (D) Vitamins
6. what corrective Asana is recommended for Kyphosis?
(a) Vajrasana and Bhujangasana
(b)Dhanurasana and Pavanmuktasana
(c) Chakrasana, Dhanurasana, and Bhujangasana [4]
(d) Matsyendrasana and Shalabhasana
7.Given below are two statements; one labeled as Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Administration squarely is a policy-making function.
Reason (R): Administration is vested with the responsibility of carrying out the broad policies laid down by the management.
Codes: (a) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(c) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
(d) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
8. What is the height of the box for Men in the Harvard Step-Up Test?
(A) 10 inches (B) 12 inches (C) 16 inches (D) 20 inches
9. Which nutrient is the chief fuel for muscular contraction?
(A) Carbohydrates (B) Fats (C) Proteins (D) Vitamins
10. Balance of an athlete will increase in all situations except-
(a) If weight of athlete increases
(b) If the centre of gravity is lowered
(c) If the centre of gravity moves away
(d) If the base is made smaller
11.Extension is the term for:
(a) Rotating around the joint
(b) Bending around the joint
(c) Extending around the joint
(d) None of the above
12. Which of the following components of fitness is NOT specifically evaluated in the SAI Khelo India Fitness Test, as described in the sources?
(a) Body Composition (b) Strength (c) Flexibility (d) Agility
13. Fartlek training method was introduced by:
(a) Hettinger (b) Adamson and Morgan (c) De Lorne (d) Gosta Holmer
14. Match the following:
15. Biomechanics is the study of ……… and their effects on living system.
(a) human movement (b) heat (c) friction (d) joints
16. SPD is a:
(a) Complete neurological disorder
(b) Physiological disorder
(c) Anatomical disorder
(d) None of the above
17. Identify the asana shown in the picture given below and choose the correct option from the following:
(a) Bhujangasana (b) Katichakrasana (c) Pawanmuktasana (d) Shalbhasana
18. which physiological change is a long-term effect of exercise on the muscular system?
(a) Accumulation of Lactate
(b) Micro-tears in muscle Fibers
(c) Increased Muscle Temperature
(d) Increased Myoglobin
SECTION – B (2*5=10)
19. Enlist the mechanical principles of equilibrium.
20. Write short note on Amenorrhoea.
21. Enlist four test items of Rikli and Jones- Senior Citizen Test.
22. State the benefits of Surya Bheda pranayama.
23. Write any two exercise guidelines given by WHO for adults.
24. What do you mean by Instrumental Aggression?
SECTION – C(3*5=15)
25. Samir is a 50-year-old male who is 171 cm in height, weighs 50 kg and has a sedentary lifestyle. He wants to lose weight and wonders how many calories he should consume each day.
26. Define circuit training. Draw the diagram of ten stations
27. Write any three advantages and disadvantages of knock-out tournaments.
28. Explain the procedure and benefits of any one asana as preventive measure for Hypertension.
29. Write about the deformities of spinal curvature.
30. What are the long-term effects of regular exercise on the cardiovascular system? Explain.
SECTION – D (4*3=12)
31.A While organizing sports events for the Annual Sports Day, Arjun and Ravi being the captain and vice-captain of sports, formed various committees as shown in the image. As Mr. Kiren Rijuju, the Sports Minister, has ordered to popularise the game of Hockey among the school students, to develop their physical remove comma add full stop, Mr. Gopi, the Physical Education Teacher of a reputed CBSE school, has decided to conduct an Inter School Hockey tournament in his school premises, after proper drawing of fixtures. He consulted the management and the Principal about the conduction of this Hockey tournament, but the PE teacher was not aware of Hockey game rules. So, he decided to watch the video clips of Paralympics and Special Olympics.
(A) To develop abilities of children with special needs, it is essential to have an educational set up that is
(a) a special school (b) a regular mainstream (c) integrated (d) an inclusive classroom
(B) Cochlear implant is not allowed in which sports?
(a) Special Olympics (b) Olympic games (c) Asian games (d) None of the above
(C) How much is the interval between two subsequent Para-Olympic games?
(a) Four years (b) Five years (c) Three years (d) Two years
(D) When were the initiated in India? Special Olympics
(α) 1987 (b) 1990 (c) 2000 (d) 1999
or
(E) In Which year, Special Olympis India was changed to Special Olympic Bharat?
(α) 2001 (b) 2000 (c) 1998 (d) 1997
32. Read the following passages and answer the questions that follow:
Rama and Deepa were our school's best badminton players. They used to practice a lot even in the off-season. Rama got an elbow injury while practising one day due to insufficient warm-ups and Deepa suffered an ankle joint sprain. They were given first assistance before being sent to the hospital.
A) The examination to be performed for bone damage is?
(a) X-ray (b) Blood test (c) ECG (d) EEG
(B) Another name for a simple fracture is? (a) Compound (b) Greenstick (c) Spiral (d) Transverse
(C) What type of injury is most likely to occur from overuse? (a) Sprain (b) Fracture (c) Tendonitis (d) Dislocation
(D) What are the factors that affect physical fitness?
(a) Strength (b) Speed (c) Endurance (d) All of the above
or (E) Sprains are injuries that happen to:
(a) Bone (b) Skin (c) Ligament (d) Muscles
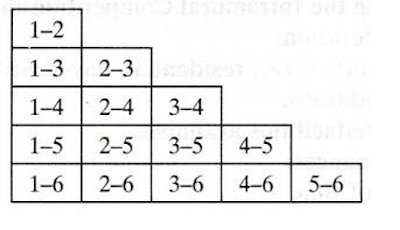
33. Below given is the Tournament fixture procedure of a CBSE Volley ball National competition
On the basis of the above data, answer the following questions:
1. The formula for calculating number of matches in Round Robin tournament are where 'N' is number of teams is
(A) N(N-1)/2 (B) N (C) (N-1)
2. In League tournaments the winner is decided by
(a) The number of matches a team loses
(b) The number of points conceded
(c) The total points accumulated from wins and draws
(d) The duration of time a team holds the lead in matches
3. Which of the following is Not a League Fixture Procedure?
(A) Ladder method (B) Elimination method (C) Cyclic method (D) Tabular method
4. Which method is shown in the picture to draw fixture in league tournament?
Or if 7 teams participate in a league Tournament, .............number of matches will be played.
SECTION – E (5*3=15)
34. Enlist the Big Five Theory Personalities and describe any three of them while comparing their characteristics.
35. What are the Nutritive and Non-nutritive components of diet? Explain
36. With the help of suitable examples, discuss the application of Newton's Laws of Motion in sports.
37. Define strength along with its types. Explain any two methods used to develop strength.
Answer Key
1 a) 2.(c) 3.a) 4.(c) 5.(A) 6.(c) 7.(c) 8.(D) 9.(A) 10.(c) 11.(c) 12.(d) 13.(d) 14.(d) 15.(a) 16.(b) 17.(a) 18(d)
SECTION – B(2*5=10)
19. The following are the mechanical principles of equilibrium:
(a) Enlarged base of support
(b) Body weight
(c) Direction of an acting force
(d) Lowered Centre of gravity
20.Amenorrhoea:
It is a menstrual disorder or illness in females in which females of 18 years of age and above either never begin menstruating or there is absence of menstruation for 3 months or more.
21.Chair Stand Test Arm Curl Test Chair Sit and Reach Test Eight Foot Up and Go Test 6-Minute Walk Test
22.Surya Bheda Pranayama activates the body and the bodily functions. It increases the digestive fire. It destroys all diseases that are caused by insufficiency of oxygen in the blood. The Gheranda Samhita says that Surya Bheda pranayama destroys decay and death, awakens Kundalini Shakti and increases digestive fire.
23.Two exercise guidelines for adults are:
i) Should do at least 150-300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity. ii) May increase moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity to more than 300 minutes
24. In instrumental aggression, harmful actions have a purpose over and above that of wounding another player. Athletes, might for instance attempt to injure an opponent because they believe that doing so will increase their chances of victory. Players do so to achieve something like a reward, prize, etc.
SECTION – C(3*5=15)
25. Calculation of BMR (a) Gender of the person - Male (b) Age of the person - 50 years (c) Height of the person - 171 cm BMR = (10 × weight in kg) + (6.25 × height in cm) - (5 × age in years) + 5 kcal/day BMR = (10 × 50 kg) + (6.25 × 171 cm) – (5 × 50 years) + 5 kcal/day BMR = 500+ 1068.75-250 + 5 BMR = 1568.75-245 BMR = 1324 kcal/day
26. Circuit training is a very popular and effective variation for the improvement of physical fitness components. In Circuit training, several exercises are done one after the other. Completion of one set of each rotation exercise is called one round. There are normally three or more rounds in a circuit training which consists of 7-12 exercises generally
27. Advantages of Knock-Out Tournaments
Cost-Effective: Knock-out tournaments are generally less expensive to organize since teams that lose are eliminated, reducing the number of matches and associated costs12.
Time Efficient: These tournaments require less time to complete due to the fewer number of matches played, allowing for a quicker resolution of the competition.
Increased Competition Level: Each match is crucial, motivating teams to perform at their best to avoid elimination, which can enhance the overall standard of play13.
Disadvantages of Knock-Out Tournaments
Elimination of Strong Teams Early: There is a risk that strong teams may be eliminated in the early rounds, which can lead to less competitive final matches12.
Potential for Weak Teams in Finals: The format may allow weaker teams to progress to the final rounds, which could diminish spectator interest and excitement23.
Reduced Engagement for Spectators: If strong teams are eliminated early, spectators may lose interest in the final matches, leading to lower attendance and engagement.
28.Tadasana, Katichakransan, Uttanpadasana, Ardha Halasana, Sarala Matyasana, Gomukhasana, UttanMandukasan-a, Vakrasana, Bhujangasana, Makarasana, Shavasana,
29. Spinal curvature deformities are conditions where the natural curve of the spine is exaggerated or altered, leading to structural and functional issues. There are three main types of spinal curvature deformities:
1. Kyphosis
Definition: Kyphosis is an excessive outward curvature of the spine, resulting in a hunchback or rounded upper back appearance. •
Causes: It can be congenital, due to poor posture, osteoporosis, or as a result of diseases like Scheuermann’s disease. •
Symptoms: Rounded back, back pain, stiffness in the spine, and in severe cases, difficulty breathing due to pressure on the lungs. •
Management: Treatment can include physical therapy, strengthening exercises (such as back extension exercises), posture correction, and in severe cases, bracing or surgery.
2. Lordosis •
Definition: Lordosis, or hyperlordosis, is an exaggerated inward curve of the lower back (lumbar spine), sometimes referred to as swayback. •
Causes: Common causes include obesity, muscle imbalance, poor posture, and spinal conditions such as spondylolisthesis. •
Symptoms: An abnormally pronounced lower back, lower back pain, and difficulty standing straight for long periods. •
Management: Physical therapy focusing on strengthening core muscles, weight management, posture correction, and stretching exercises. Severe cases might require bracing or surgical intervention.
3. Scoliosis •
Definition: Scoliosis is a lateral or sideways curvature of the spine, often forming an "S" or "C" shape when viewed from the back. •
Causes: It can be idiopathic (unknown cause), congenital (due to malformations during development), or neuromuscular (associated with conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy). •
Symptoms: Uneven shoulders or hips, one shoulder blade more prominent than the other, and potential back pain. Severe scoliosis can impact lung and heart function. •
Management: Treatments range from observation in mild cases to bracing for moderate cases, and surgery (such as spinal fusion) for severe cases.
30. long-term effects of regular exercise on the cardiovascular system
1. Improved Heart Efficiency •
Increased Cardiac Output: Regular exercise enhances the ability of the heart to pump blood. This increase in cardiac output means the heart can supply more oxygen and nutrients to muscles during physical activity. •
Stronger Heart Muscle: The heart becomes stronger and more efficient at pumping blood, requiring fewer beats per minute (lower resting heart rate) to maintain circulation.
2. Lower Resting Heart Rate •
Bradycardia in Athletes: Over time, regular exercise results in a lower resting heart rate (known as bradycardia in well-trained athletes). This reflects the heart’s increased efficiency and reduced workload during rest. •
Enhanced Stroke Volume: The amount of blood pumped out of the heart with each beat (stroke volume) increases, allowing the heart to pump more effectively with less effort.
3. Reduced Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases •
Lower Blood Pressure: Regular exercise helps to maintain healthy blood pressure levels, reducing the risk of hypertension. •
Improved Blood Lipid Profile: Exercise can lower "bad" LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels while increasing "good" HDL cholesterol, which helps protect against plaque buildup in arteries. •
Prevention of Atherosclerosis: The reduction in cholesterol and better blood flow reduce the risk of developing atherosclerosis (narrowing of arteries).
4. Enhanced Blood Circulation and Vessel Health •
Improved Endothelial Function: The endothelial cells lining the blood vessels become more efficient, aiding in better dilation and contraction of blood vessels, which improves overall circulation. • Increased Capillarization: Regular aerobic activity promotes the growth of new capillaries in muscles and heart tissue, enhancing blood flow and oxygen delivery. •
Reduced Risk of Blood Clots: Exercise helps maintain optimal blood viscosity and reduces the risk of clot formation.
5. Regulation of Blood Sugar and Reduced Inflammation •
Better Blood Glucose Management: Regular physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity and helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. •
Reduced Systemic Inflammation: Exercise has anti-inflammatory effects, which can lower the risk of chronic cardiovascular conditions related to inflammation.
6. Improved Recovery and Adaptation •
Faster Recovery: A well-trained cardiovascular system can recover more quickly after exertion, as it becomes more efficient in managing oxygen and nutrient delivery. •
Better VO2 Max: Regular aerobic exercise increases maximal oxygen uptake (VO2 max), which is an indicator of cardiovascular f itness and endurance.




Comments
Post a Comment